This module addresses the critical challenge of securing endpoints in modern networks where traditional boundaries have blurred. Students will explore how the proliferation of mobile devices, IoT endpoints, and BYOD policies has transformed endpoint security requirements, and learn about comprehensive protection strategies including Network Access Control (NAC), Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE), and 802.1X port-based authentication.
📋 Overview
🔑 Key Terms
Endpoint
Any device that connects to the network, including PCs, servers, mobile devices, IoT devices, and network cameras.
NAC
Network Access Control - system that checks endpoint compliance with security policies before granting network access.
Cisco ISE
Identity Services Engine - combines AAA and NAC functionality into a single comprehensive system.
802.1X
IEEE standard for port-based network access control and authentication protocol.
Supplicant
Client device requesting network access in 802.1X authentication process.
Authenticator
Network device (typically switch) controlling physical access based on authentication status.
Endpoint Evolution
Traditional vs Modern Endpoints
Traditional Endpoints
Legacy network endpoints with predictable security requirements:
- Desktop PCs and workstations
- Servers and network printers
- Fixed network locations
- Corporate-owned and managed
- Standardized operating systems
Modern Endpoints
Contemporary devices that have blurred network boundaries:
- Smartphones and tablets
- Laptops and wearable devices
- IoT devices and network cameras
- BYOD and personal devices
- Multiple connectivity methods
Blurred Network Boundaries
Modern endpoints can access network resources from multiple locations using various connectivity methods at any time, making traditional perimeter-based security insufficient.
Endpoint Security Evolution
Traditional endpoint security relied primarily on host-based measures:
- Antimalware software
- Host-based IPS (HIPS)
- Host-based firewall software
- Local data encryption
Protection Methods
Enhanced Security Technologies
Email Security Appliances (ESA)
Comprehensive email protection:
- Anti-spam and anti-phishing
- Malware detection and blocking
- Data loss prevention
- Email encryption capabilities
Web Security Appliances (WSA)
Advanced web traffic protection:
- URL filtering and categorization
- Malware scanning
- Application visibility and control
- Bandwidth management
Data Protection Methods
BitLocker and Drive Encryption
Endpoints can be protected from data loss through encryption at file, folder, or drive level. Microsoft Windows 10 includes BitLocker for full-disk encryption, protecting data even if devices are lost or stolen.
| Protection Layer | Technology | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Host-based | Antimalware, HIPS, Firewall | Local endpoint protection |
| Network-based | ESA, WSA, IPS | Traffic inspection and filtering |
| Access Control | NAC, ISE, 802.1X | Authentication and authorization |
| Data Protection | BitLocker, File Encryption | Data confidentiality |
NAC and Cisco ISE
Network Access Control (NAC)
Policy Compliance Checking
NAC systems check whether endpoints attempting network access comply with security policies, handling user authentication and taking action against devices that violate policies through outdated security software.
NAC Capabilities
- Compliance Assessment: Evaluates endpoint security posture
- Policy Enforcement: Blocks non-compliant devices
- Remediation: Brings devices up to compliance standards
- Guest Access: Provides managed network access for visitors
- Quarantine: Isolates non-compliant devices
Traditional NAC
Standalone network access control:
- Separate authentication systems
- Limited integration capabilities
- Complex management overhead
- Multiple policy engines
Cisco ISE
Integrated identity and access management:
- Combined AAA and NAC functionality
- Centralized policy management
- Context-aware access control
- Comprehensive visibility and reporting
Cisco ISE Benefits
By combining AAA and NAC into a single system, Cisco ISE provides streamlined management, consistent policy enforcement, and comprehensive visibility across the entire network infrastructure.
🔐 802.1X Authentication
Port-Based Access Control
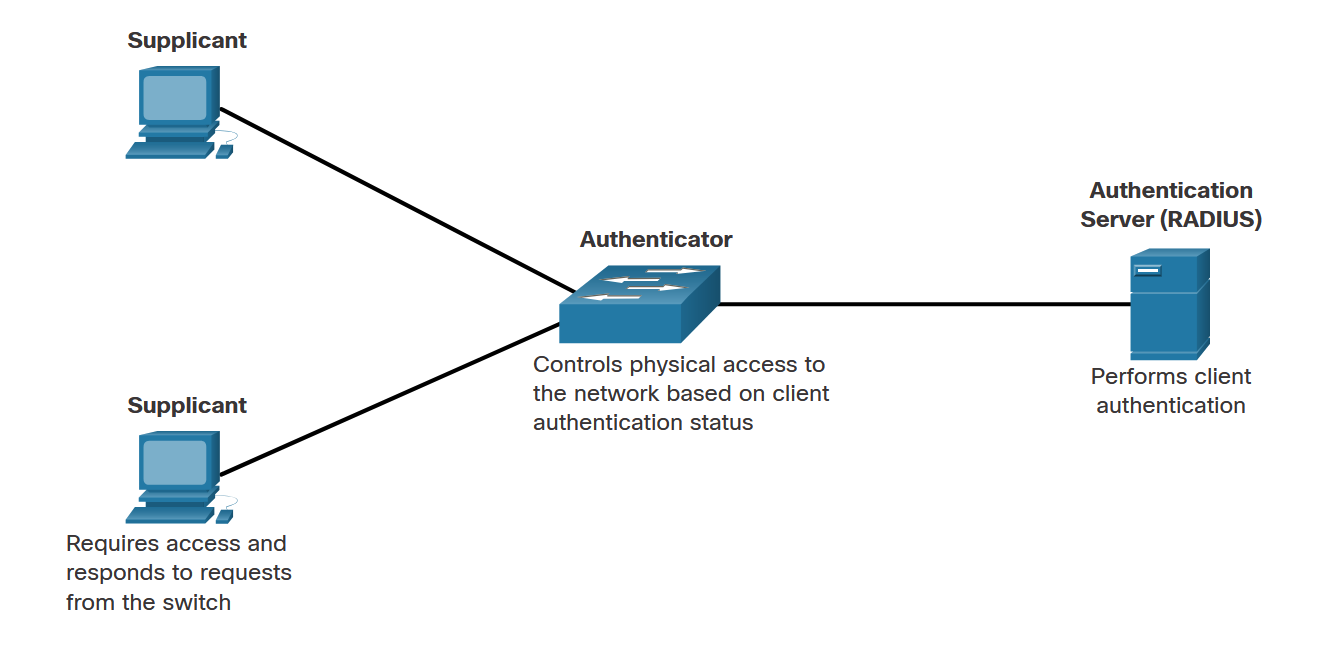
IEEE 802.1X defines a port-based access control and authentication protocol that restricts unauthorized workstations from connecting to a LAN through publicly accessible switch ports.
802.1X Roles
Supplicant (Client)
The device requesting network access:
- Workstation or endpoint device
- Runs 802.1X-compliant client software
- Responds to authentication requests
- Initiates access requests
Authenticator (Switch)
Controls physical network access:
- Acts as intermediary (proxy)
- Controls port access based on auth status
- Uses RADIUS software agent
- Encapsulates/de-encapsulates EAP
Authentication Server
Performs client authentication:
- Typically RADIUS server
- Validates client credentials
- Returns authentication decisions
- Provides authorization policies
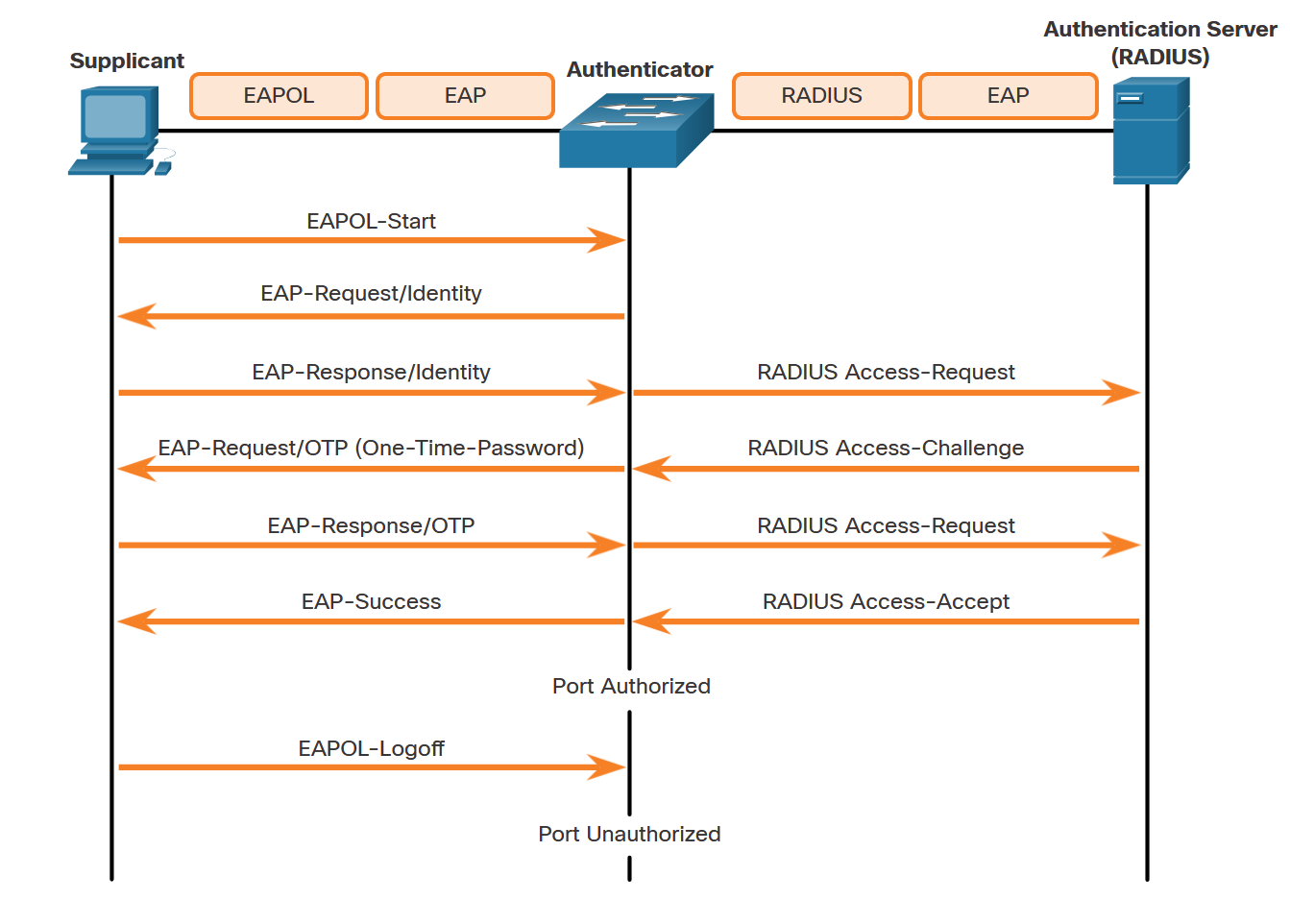
Authentication Process
EAP and RADIUS Communication
The system uses EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) and EAPOL to carry authentication traffic between client and switch, while the switch uses EAP and RADIUS to communicate with the authentication server.
Port Control States
| State | Description | Access Level |
|---|---|---|
| Auto | Port performs authentication process | Based on authentication result |
| Force-Authorized | Port provides authorized access | Full network access |
| Force-Unauthorized | Port denies all access | No network connectivity |
📚 Case Study: BYOD Implementation
University BYOD Network
A large university implements Cisco ISE with 802.1X authentication to support 15,000 students and staff with personal devices. The solution provides automatic device profiling, policy-based network segmentation, and guest access management while maintaining security compliance and reducing IT support overhead by 40%.
The implementation demonstrates how modern endpoint security solutions can accommodate diverse device types while maintaining security policies, providing seamless user experience, and enabling comprehensive network visibility and control.
⚠️ Common Pitfalls & Misconceptions
Relying Solely on Perimeter Security
Assuming traditional perimeter defenses are sufficient for modern endpoint security without implementing endpoint-specific protections.
One-Size-Fits-All Policies
Applying identical security policies to all endpoint types without considering device capabilities and use cases.
Layered Endpoint Security
Implement multiple security layers including host-based protection, network access control, and data encryption for comprehensive endpoint security.
✅ Quick Checks
- How have modern endpoints changed network security requirements?
Modern endpoints like smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices have blurred network boundaries by enabling access from multiple locations using various connectivity methods, requiring new security approaches beyond traditional perimeter defense. - What is the primary function of Network Access Control (NAC)?
NAC checks whether endpoints attempting network access comply with security policies, handles authentication, and can take action against non-compliant devices or bring them up to compliance standards. - What are the three roles in 802.1X authentication?
Supplicant (client device requesting access), Authenticator (switch controlling port access), and Authentication Server (typically RADIUS server validating credentials). - How does Cisco ISE differ from traditional NAC solutions?
Cisco ISE combines AAA and NAC functionality into a single system, providing centralized policy management, context-aware access control, and comprehensive visibility. - What protocols are used in 802.1X authentication?
EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) and EAPOL for client-to-switch communication, and EAP with RADIUS for switch-to-server communication.
📝 Summary
- Modern endpoints include traditional devices plus smartphones, tablets, IoT devices, and wearables
- Endpoint security has evolved from host-based protection to comprehensive network access control
- NAC systems check endpoint compliance and enforce security policies before granting access
- Cisco ISE combines AAA and NAC functionality for streamlined identity and access management
- 802.1X provides port-based authentication using supplicant, authenticator, and authentication server roles
- EAP and RADIUS protocols enable secure authentication communication
- Data protection includes local encryption solutions like BitLocker for drive-level security
- Layered security approach combines host-based, network-based, and access control technologies