This module provides hands-on implementation of site-to-site IPsec VPNs using Cisco CLI commands. Students will learn the five-step IPsec negotiation process, configure ISAKMP policies for IKE Phase 1, define IPsec policies for Phase 2, create crypto maps to bind configurations, and test VPN functionality. The focus is on practical configuration using pre-shared key authentication between two sites.
📋 Overview
🔑 Key Terms
ISAKMP
Internet Security Association Key Management Protocol - manages IPsec security associations.
Interesting Traffic
Network traffic that matches ACL criteria and triggers IPsec tunnel establishment.
IKE Phase 1
Initial negotiation phase establishing secure ISAKMP tunnel for management traffic.
IKE Phase 2
Second phase negotiating IPsec security associations for data traffic protection.
Crypto Map
Configuration that binds IPsec policies, transform sets, and peer information together.
Transform Set
Combination of encryption and authentication algorithms for IPsec data protection.
IPsec Negotiation Process
Five-Step IPsec Negotiation
IKE Phase 1 and Phase 2
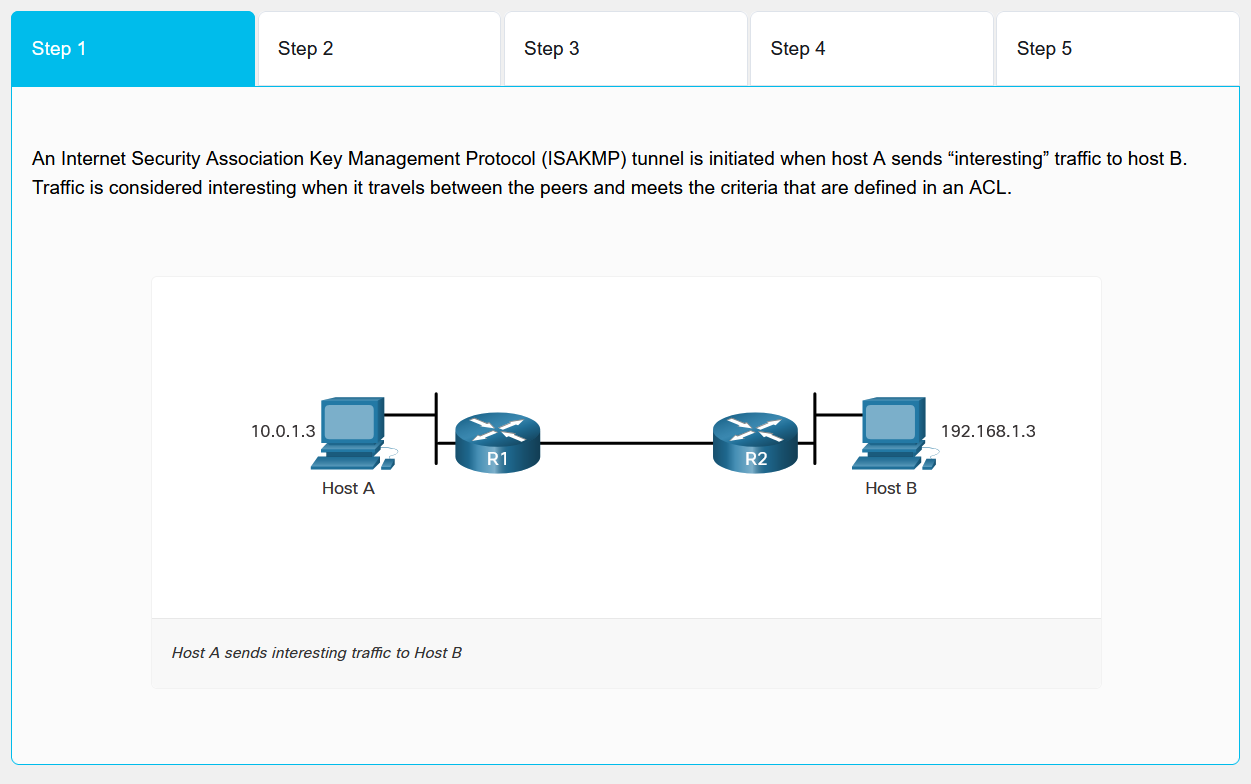
IPsec VPN tunnel establishment involves five steps divided into two phases. An ISAKMP tunnel is initiated when Host A sends "interesting" traffic to Host B that matches criteria defined in an ACL.
Step-by-Step Process
- Interesting Traffic Detection: Traffic matching ACL criteria triggers tunnel initiation
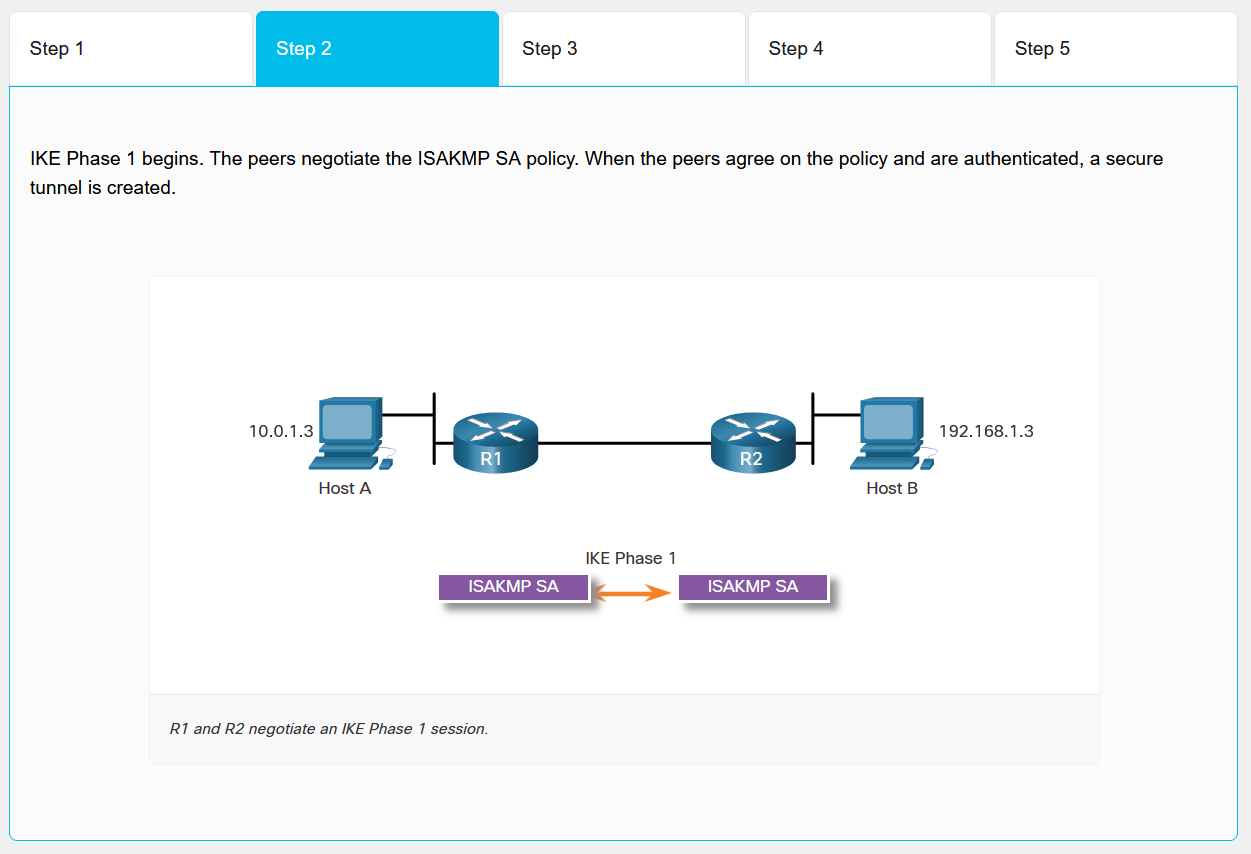
- IKE Phase 1 Negotiation: Peers negotiate ISAKMP SA policy for secure management channel
- IKE Phase 1 Completion: Secure tunnel created after policy agreement and authentication
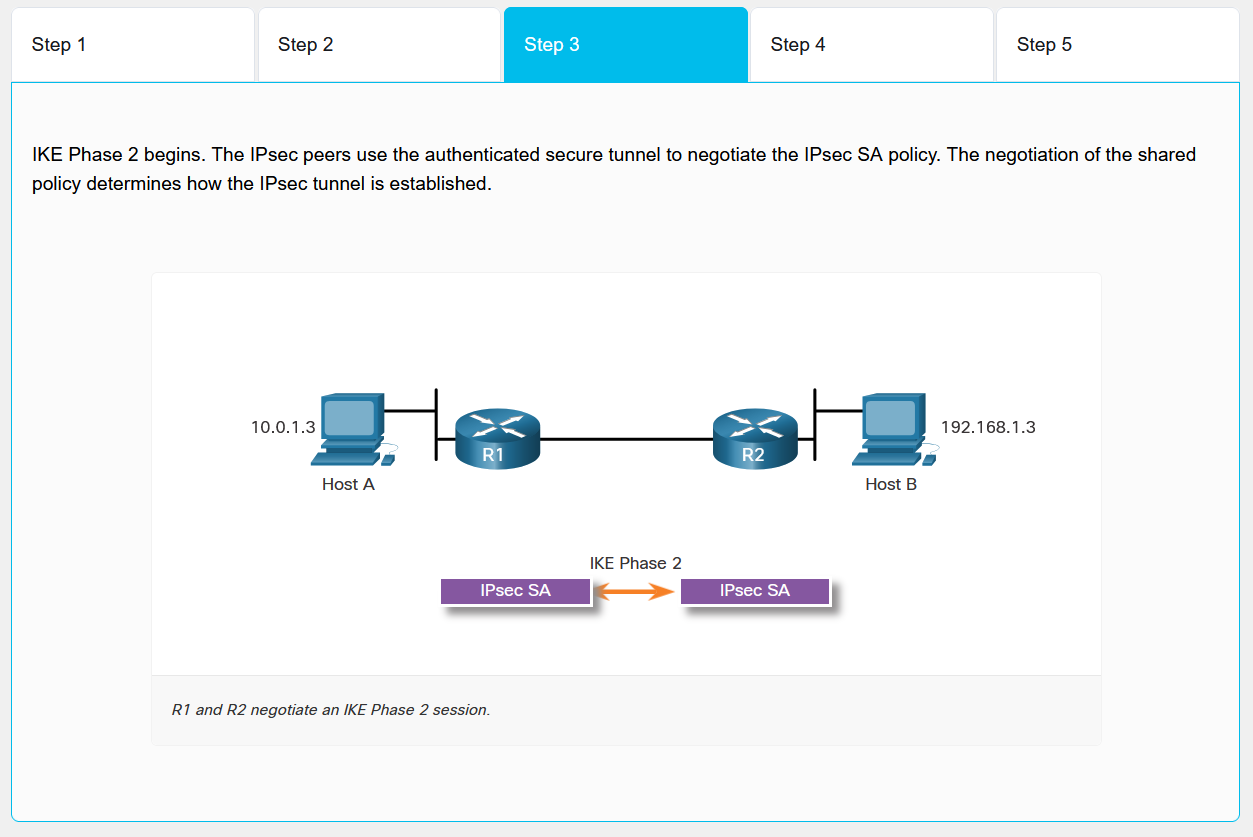
- IKE Phase 2 Negotiation: IPsec peers negotiate IPsec SA policy through secure tunnel
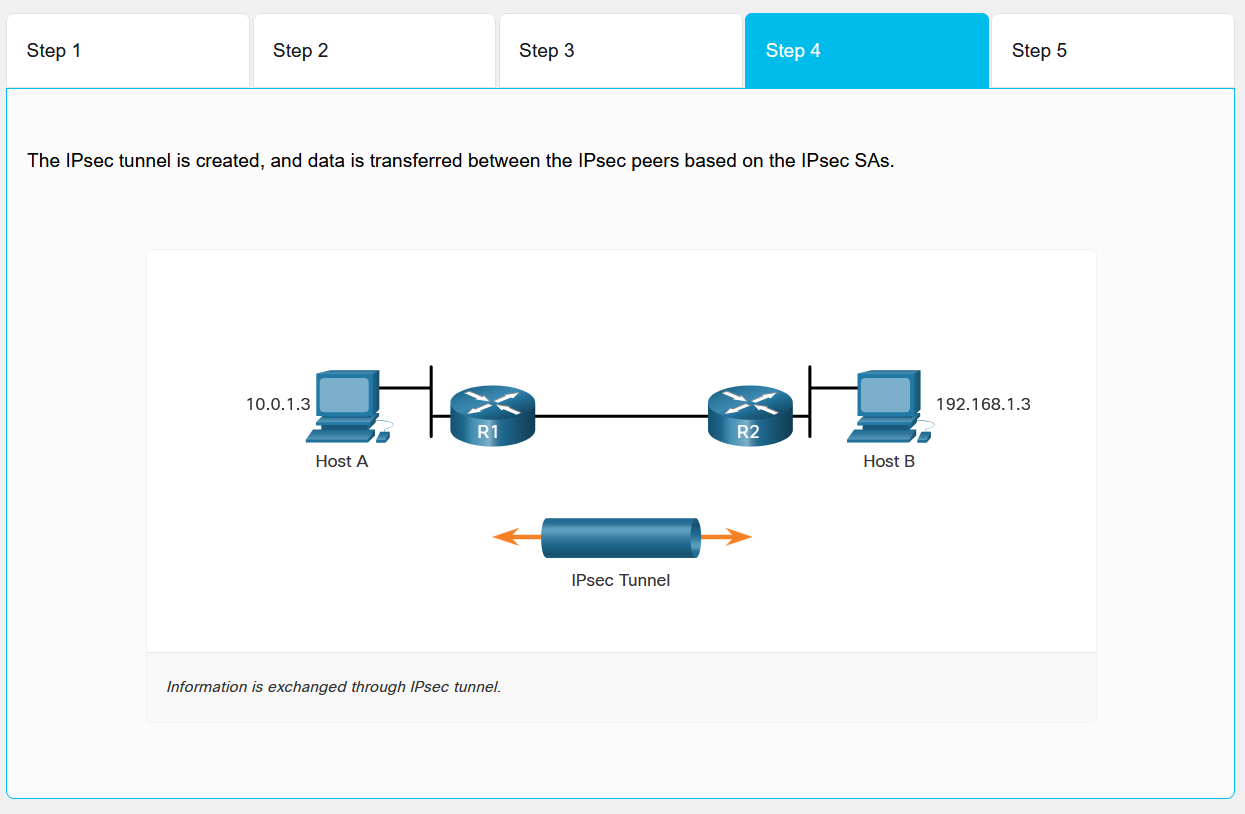
- Data Transfer: IPsec tunnel established for secure data transmission
Phase Comparison
| Aspect | IKE Phase 1 | IKE Phase 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Establish secure management channel | Negotiate data protection parameters |
| Protocol | ISAKMP | IPsec |
| Authentication | Peer identity verification | Data origin authentication |
| Result | ISAKMP SA established | IPsec SA established |
Tunnel Termination
IPsec tunnels terminate when:
- IPsec SAs are manually deleted
- SA lifetime expires
- Network connectivity is lost
- Configuration changes require renegotiation
⚙️ ISAKMP Policy Configuration
Default ISAKMP Policies
Cisco IOS Defaults
Cisco IOS comes with default ISAKMP policies already configured. These can be viewed using the show crypto isakmp default policy command and provide a secure starting point for VPN configuration.
Default Policy Parameters
R1# show crypto isakmp default policy
Default IKE policy
Default protection suite of priority 65507
encryption algorithm: AES - Advanced Encryption Standard (128 bit keys)
hash algorithm: Secure Hash Standard
authentication method: Rivest-Shamir-Adleman SignatureISAKMP Policy Components
Encryption Algorithm
Protects ISAKMP negotiations:
- AES (128, 192, 256-bit)
- 3DES (legacy)
- DES (deprecated)
Hash Algorithm
Ensures message integrity:
- SHA-1 (legacy)
- SHA-256 (recommended)
- MD5 (deprecated)
Authentication Method
Verifies peer identity:
- Pre-shared keys
- RSA signatures
- RSA encrypted nonces
Diffie-Hellman Group
Key exchange strength:
- Group 1 (768-bit)
- Group 2 (1024-bit)
- Group 5 (1536-bit)
Custom ISAKMP Policy Configuration
Router(config)# crypto isakmp policy 10
Router(config-isakmp)# encryption aes 256
Router(config-isakmp)# hash sha256
Router(config-isakmp)# authentication pre-share
Router(config-isakmp)# group 5
Router(config-isakmp)# lifetime 86400Pre-Shared Key Configuration
Router(config)# crypto isakmp key cisco123 address 172.30.2.2⚙️ IPsec Policy Configuration
Defining Interesting Traffic
Access Control Lists
Interesting traffic must be defined before IKE Phase 1 negotiations can begin. For site-to-site VPNs, interesting traffic is typically any permitted communications between the site LANs.
ACL Configuration Example
R1(config)# access-list 101 permit ip 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
R2(config)# access-list 101 permit ip 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 10.0.1.0 0.0.0.255Transform Set Configuration
Transform sets define the encryption and authentication algorithms for data protection:
Router(config)# crypto ipsec transform-set MYSET esp-aes 256 esp-sha-hmac
Router(cfg-crypto-trans)# mode tunnelTransform Set Options
| Category | Options | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | esp-aes, esp-3des, esp-des | esp-aes 256 |
| Authentication | esp-sha-hmac, esp-md5-hmac | esp-sha-hmac |
| Mode | tunnel, transport | tunnel (for site-to-site) |
Verification Commands
R1# show crypto isakmp sa
IPv4 Crypto ISAKMP SA
dst src state conn-id status
R1# show crypto ipsec transform-set⚙️ Crypto Map Configuration
Crypto Map Purpose
Policy Integration
Crypto maps bind together the interesting traffic definition, IPsec transform sets, and peer information into a complete IPsec policy that can be applied to interfaces.
Crypto Map Syntax
Router(config)# crypto map map-name seq-num { ipsec-isakmp | ipsec-manual }Parameter Descriptions
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| map-name | Identifies the crypto map set |
| seq-num | Sequence number for crypto map entry |
| ipsec-isakmp | Indicates IKE will establish IPsec SAs |
| ipsec-manual | Manual SA configuration (not recommended) |
Complete Crypto Map Configuration
Router(config)# crypto map MYMAP 10 ipsec-isakmp
Router(config-crypto-map)# set peer 172.30.2.2
Router(config-crypto-map)# set transform-set MYSET
Router(config-crypto-map)# match address 101Interface Application
Router(config)# interface serial0/0/0
Router(config-if)# crypto map MYMAPCrypto Map Components
- Peer Address: Remote VPN gateway IP address
- Transform Set: Encryption and authentication algorithms
- Access List: Defines interesting traffic
- Lifetime: SA duration before renegotiation
🧪 Testing and Verification
Sending Interesting Traffic
Extended Ping
Use extended ping to test VPN configuration by sending traffic from one LAN interface to another. The first ping may fail as it takes time to establish ISAKMP and IPsec tunnels.
Extended Ping Example
R1# ping 192.168.1.1 source 10.0.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 10.0.1.1
.!!!!
Success rate is 80 percent (4/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 msVerification Commands
ISAKMP SA Status
R1# show crypto isakmp sa
R1# show crypto isakmp sa detailIPsec SA Status
R1# show crypto ipsec sa
R1# show crypto ipsec sa detailCrypto Map Status
R1# show crypto map
R1# show crypto map interfaceDebug Commands
R1# debug crypto isakmp
R1# debug crypto ipsecTroubleshooting Common Issues
- Mismatched Policies: Ensure ISAKMP and IPsec policies match on both peers
- Incorrect ACLs: Verify interesting traffic definitions are mirror images
- Wrong Peer Address: Check crypto map peer configuration
- Pre-shared Key Mismatch: Verify identical keys on both routers
- Interface Application: Ensure crypto map applied to correct interface
GRE over IPsec
Protocol Limitations
IPsec only supports unicast traffic. For multicast routing protocols, configure GRE tunnel for multicast traffic. GRE supports multiprotocol tunneling but does not provide encryption.
📚 Case Study: XYZCORP Site-to-Site VPN
Two-Site Corporate Network
XYZCORP implements site-to-site IPsec VPN between headquarters (10.0.1.0/24) and branch office (192.168.1.0/24) using pre-shared key authentication. The configuration includes ISAKMP policies, transform sets, and crypto maps on both R1 and R2 routers.
This implementation demonstrates practical IPsec VPN deployment, showing how the five-step negotiation process works in real networks and the importance of matching configurations on both peers for successful tunnel establishment.
⚠️ Common Pitfalls & Misconceptions
Asymmetric ACL Configuration
Creating ACLs that don't mirror each other on both peers, preventing proper interesting traffic identification.
Immediate Tunnel Establishment
Expecting tunnels to be established immediately after configuration without sending interesting traffic to trigger negotiation.
Systematic Configuration
Follow the five-step process systematically, verify each step before proceeding, and use debug commands for troubleshooting.
✅ Quick Checks
- What are the five steps of IPsec negotiation?
1) Interesting traffic detection, 2) IKE Phase 1 negotiation, 3) IKE Phase 1 completion, 4) IKE Phase 2 negotiation, 5) Data transfer through IPsec tunnel. - What triggers the initiation of an ISAKMP tunnel?
Interesting traffic that matches criteria defined in an ACL traveling between IPsec peers. - What is the purpose of a crypto map?
To bind together interesting traffic definitions, IPsec transform sets, and peer information into a complete IPsec policy. - Why might the first ping fail when testing a new VPN?
It takes a few milliseconds to establish the ISAKMP and IPsec tunnels after interesting traffic is detected. - What additional configuration is needed for multicast traffic over IPsec?
GRE tunnel configuration, as IPsec only supports unicast traffic and GRE provides multiprotocol tunneling support.
📝 Summary
- IPsec negotiation involves five steps divided into IKE Phase 1 and Phase 2
- ISAKMP policies define security parameters for IKE Phase 1 tunnel establishment
- Interesting traffic defined by ACLs triggers IPsec tunnel negotiation
- Transform sets specify encryption and authentication algorithms for data protection
- Crypto maps bind all IPsec components together and apply to interfaces
- Extended ping tests VPN functionality by sending traffic between LANs
- Multiple verification commands help troubleshoot IPsec implementations
- GRE over IPsec required for multicast routing protocol support