This module introduces the Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) family of next-generation firewall devices. Students will learn about different ASA models, their capabilities, and deployment scenarios. The module covers hardware specifications, virtual appliance options, and the ASA 5506-X with FirePOWER Services as a comprehensive security solution for small to medium businesses.
📋 Overview
🔑 Key Terms
ASA
Adaptive Security Appliance - Cisco's dedicated firewall and VPN security platform.
NGFW
Next-Generation Firewall - advanced firewall with integrated threat defense capabilities.
FirePOWER Services
Integrated threat defense services providing advanced malware protection and intrusion prevention.
ASAv
Adaptive Security Virtual Appliance - virtualized version of ASA firewall functionality.
Security Levels
Numerical values (0-100) assigned to interfaces to distinguish trust levels between networks.
Stateful Inspection
Firewall technology that tracks connection states and allows return traffic automatically.
ASA Solutions
ASA vs IOS Router Firewalls
Dedicated vs Integrated Solutions
IOS router firewall solutions are appropriate for small branch deployments and administrators experienced with Cisco IOS. However, IOS firewalls don't scale well and typically cannot meet large enterprise needs, making dedicated ASA appliances the preferred choice.
ASA with FirePOWER Services
The Cisco ASA with FirePOWER Services family provides dedicated firewall services in next-generation firewall (NGFW) devices that deliver integrated threat defense across the entire attack continuum.
Model Selection Criteria
The choice of ASA model depends on organizational requirements:
- Maximum Throughput: Stateful inspection performance requirements
- Maximum Connections per Second: New connection establishment rate
- Interface Requirements: Number and types of network interfaces needed
- Budget Constraints: Cost considerations for hardware and licensing
- Advanced Features: VPN capacity, high availability, and threat services
Network Terminology
Outside Network
Untrusted network segment:
- Typically the internet
- Security level 0
- Highest threat potential
- Requires strict access controls
Inside Network
Trusted internal network:
- Corporate LAN
- Security level 100
- Highest trust level
- Outbound access allowed by default
DMZ
Demilitarized Zone:
- Semi-trusted network segment
- Security levels 1-99
- Hosts public-facing servers
- Controlled access from inside/outside
Advanced ASA Features
- ASA Virtualization: Multiple security contexts on single appliance
- High Availability: Failover capabilities for business continuity
- Identity Firewall: User-based access control policies
- Threat Control: Integrated malware protection and intrusion prevention
- Containment Services: Advanced threat isolation and remediation
Firepower Models
Cisco Firepower Series
All ASA models provide advanced stateful firewall features and VPN functionality. The primary differences are maximum traffic throughput and interface capabilities.
Cisco Firepower 1000
Entry-level NGFW for small businesses:
- Suitable for SOHO and small business
- Cost-effective security solution
- Essential firewall and VPN features
- Limited throughput capacity
Cisco Firepower 2100
Mid-range security appliance:
- Branch office and medium business
- Enhanced performance capabilities
- Advanced threat protection
- Scalable interface options
Cisco Firepower 4100
High-performance enterprise solution:
- Large enterprise deployments
- High-throughput requirements
- Advanced security services
- Modular architecture
Cisco Firepower 9300
Data center and service provider:
- Maximum performance and scalability
- Carrier-grade reliability
- Advanced threat intelligence
- Multi-tenant capabilities
Performance Considerations
| Model Series | Target Deployment | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Firepower 1000 | Small Office/Home Office | Basic firewall, VPN, threat protection |
| Firepower 2100 | Branch/Medium Business | Enhanced performance, advanced features |
| Firepower 4100 | Large Enterprise | High throughput, modular design |
| Firepower 9300 | Data Center/Service Provider | Maximum scalability, multi-tenancy |
Virtual ASA (ASAv)
Virtualization Benefits
ASA in the Virtual Domain
The Cisco ASAv brings ASA appliance power to virtual environments, operating as a VM using server interfaces to process traffic. It supports modern x86 server virtualization infrastructure.
ASAv Capabilities
Like physical ASA devices, the ASAv supports:
- Site-to-Site VPN: IPsec tunnels between locations
- Remote-Access VPN: SSL and IPsec client connections
- Clientless VPN: Browser-based secure access
- Stateful Firewall: Advanced packet inspection
- Threat Services: Integrated security features
ASAv Limitations
Unsupported Features
The ASAv does not support clustering and multiple contexts, which are available on physical ASA appliances.
ASAv Model Options
| Model | Memory Requirement | Throughput | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASAv5 | 2 GB | Up to 100 Mbps | Small deployments |
| ASAv10 | 4 GB | Up to 1 Gbps | Medium deployments |
| ASAv30 | 8 GB | Up to 2 Gbps | Large deployments |
| ASAv50 | 16 GB | Up to 10 Gbps | Enterprise deployments |
| ASAv100 | 32 GB | Up to 20 Gbps | High-performance virtual |
Deployment Scenarios
- Cloud Environments: AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform
- Private Cloud: VMware vSphere, Microsoft Hyper-V
- Hybrid Deployments: Mixed physical and virtual infrastructure
- Development/Testing: Lab environments and proof-of-concept
ASA 5506-X with FirePOWER
Overview
Small Business Solution
The Cisco ASA 5506-X is a full-featured security appliance for small businesses, branch offices, and enterprise teleworker environments, delivering high-performance firewall, SSL VPN, IPsec VPN, and rich networking services in a modular, plug-and-play appliance.
Hardware Specifications
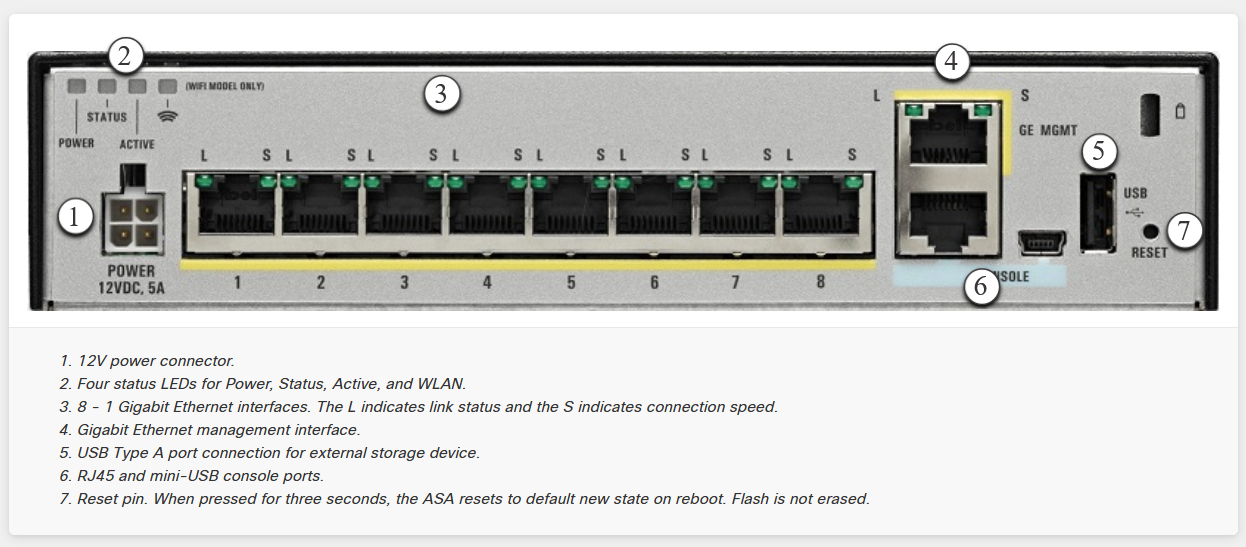
Front Panel Features
User-accessible components:
- Power and status indicators
- Network activity LEDs
- Easy visual monitoring
- Compact form factor
Back Panel Connectivity
Interface and power connections:
- 8 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
- Dedicated management interface
- Console ports (RJ45 and mini-USB)
- USB Type A for external storage
Technical Specifications
- Default DRAM: 4 GB memory
- Internal Flash: 8 GB storage
- Network Interfaces: 8 x 1 Gigabit Ethernet
- Management Interface: Dedicated Gigabit Ethernet
- Console Access: RJ45 and mini-USB ports
- Power: 12V external power adapter
Security Levels
Interface Security Assignment
The ASA assigns security levels (0-100) to distinguish between inside and outside networks. Higher numbers indicate higher trust levels, with outbound traffic allowed and inspected by default.
Failover Configuration
High availability requirements:
- Two units must be identical models
- Same hardware configuration required
- Identical number and types of interfaces
- Same amount of RAM
- Security Plus license required
Edge Security Deployment
ISP Connection
The ASA 5506-X is commonly used as an edge security device, connecting small businesses to ISP devices such as DSL or cable modems for internet access while providing comprehensive security services.
Interface Modes
Two Operating Modes
Routed Mode
Layer 3 network separation:
- Two or more interfaces separate Layer 3 networks
- Each interface in different IP subnet
- ASA acts as router hop
- Default operating mode
- Full routing capabilities
Transparent Mode
Layer 2 bridge operation:
- "Bump in the wire" deployment
- "Stealth firewall" operation
- Functions like Layer 2 device
- Not considered router hop
- Invisible to network topology
Mode Selection Criteria
| Consideration | Routed Mode | Transparent Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Network Changes | Requires IP addressing changes | No IP addressing changes |
| Routing | Full routing capabilities | Limited routing features |
| Deployment | Network redesign may be needed | Easy insertion into existing network |
| Management | Standard IP management | Special management considerations |
Licensing Options
Base vs Security Plus
Most ASA appliances come pre-installed with either a Base license (basic features) or Security Plus license (advanced features including failover, VPN capacity increases, and additional security services).
📚 Case Study: Small Business Security
Professional Services Firm
A 50-employee professional services firm deploys ASA 5506-X with FirePOWER Services to replace aging router-based firewall. The solution provides integrated threat protection, SSL VPN for remote workers, and site-to-site VPN to branch office, improving security posture while reducing management complexity.
This deployment demonstrates how modern ASA appliances provide enterprise-grade security features in small business environments, offering scalability and advanced threat protection previously available only in larger organizations.
⚠️ Common Pitfalls & Misconceptions
Undersizing ASA Model
Selecting ASA model based only on current needs without considering future growth and peak traffic requirements.
Virtual vs Physical Performance
Assuming ASAv provides identical performance to physical appliances without considering hypervisor overhead and resource allocation.
Proper Sizing and Planning
Evaluate throughput requirements, connection rates, and feature needs carefully, including future growth projections and peak usage scenarios.
✅ Quick Checks
- What are the main factors in selecting an ASA model?
Maximum throughput requirements, maximum connections per second, interface needs, budget constraints, and required advanced features. - What is the difference between routed and transparent mode?
Routed mode separates Layer 3 networks with the ASA acting as a router hop, while transparent mode operates as a "bump in the wire" Layer 2 device. - What are the limitations of ASAv compared to physical ASA?
ASAv does not support clustering and multiple contexts, which are available on physical ASA appliances. - What security levels does the ASA use?
Security levels range from 0 (untrustworthy/outside) to 100 (very trustworthy/inside), with DMZ typically using levels 1-99. - What is required for ASA failover configuration?
Two identical ASA units with same hardware configuration, interfaces, RAM, and Security Plus license.
📝 Summary
- ASA provides dedicated firewall services superior to IOS router firewalls for enterprise needs
- Firepower series offers models from small business (1000) to data center (9300) deployments
- ASAv brings ASA capabilities to virtual environments with five performance tiers
- ASA 5506-X provides full-featured security for small businesses and branch offices
- Security levels (0-100) distinguish trust levels between network segments
- Routed mode provides Layer 3 separation while transparent mode offers Layer 2 operation
- Advanced features include virtualization, high availability, identity firewall, and threat services
- Proper model selection requires careful evaluation of performance and feature requirements